OrdSys’s backend, built with Django, structures its data using a set of interconnected tables. Each table defines a specific entity in the system. The file ./backend/models.py contains the declarations and relationships of these tables.
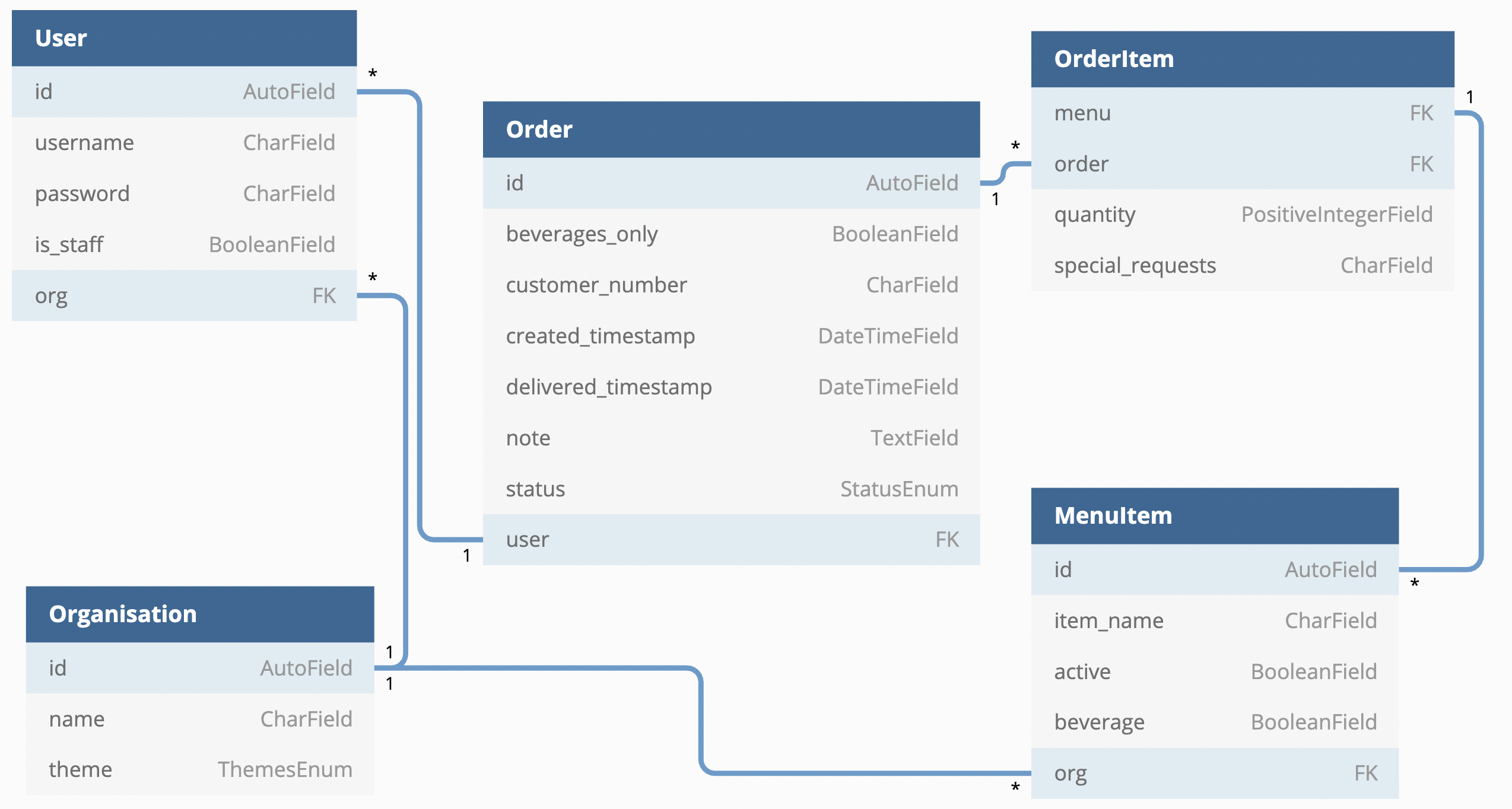
Below is an expanded overview of each table and its key components:
User Table #
This table holds information about user accounts. It replaces Django’s default user system. Attributes include:
- id: A unique number assigned to each user.
- username: The name chosen by the user.
- password: A secure, encrypted version of the user’s password.
- is_staff: Indicates if the user can access the admin interface.
- org: Links to the organization the user is part of.
Order Table #
This table stores basic details about orders like customer number and status. Order contents are in the OrderItem table. For example, if a customer orders a hamburger and soda, the Order table records the customer’s number, while the OrderItem table links the hamburger and soda to the order using its id.
If someone places an order for a hamburger and a soda to customer #23, a row will be added to the Order table with customer number 23, and two rows will be added to the OrderItem table connecting a soda and a hamburger to the order in the Order table using its ID.
Attributes include:
- id: A unique order number.
- beverages_only: Shows if the order is only for drinks.
- customer_number: The customer identifier.
- created_timestamp: When the order was made.
- delivered_timestamp: When the order was delivered (optional).
- note: Additional customer information (optional).
- status: The current state of the order.
- user: The user who created the order.
The OrderItem table #
This table details the items in an order. Each row represents an amount of a menu item along with special requests, if any, and links to an order in the Order table.
It’s important to note that deleting an order or menu item will also remove associated items in the OrderItem table due to cascading deletion. To avoid losing data, deactivate menu items instead of deleting them when necessary.
Attributes include:
- menu: The menu item’s id.
- order: The order id the item belongs to.
- quantity: How many of the menu item were ordered.
- special_requests: Any specific customer requests for the menu item (optional).
MenuItem Table #
This table lists all possible items for ordering, whether they are food or drinks. Items can be set as active (visible) or inactive (hidden).
Attributes include:
- id: A unique menu item number.
- item_name: The name of the item.
- active: If the item should be shown for ordering.
- beverage: If the item is a drink.
- org: The organization the item is associated with.
Organization Table #
Organizations in the system have their own table, which defines each one by name and the theme users will see. The only information an organisation inherently contains is a name and which theme users belonging to that organisation should use, but they are used in many parts of the system to separate data.
Every user must belong to an organization. If you ever reset the database, you’ll need to create an organization first before adding a superuser. Use the createorganisation command in manage.py for this.
Attributes include:
- id: A unique organization number.
- name: The organization’s name.
- theme: The visual theme used for the organization’s interface.